Antique Arms & Militaria
A Fine & Rare Original Heavy Grade Imperial Roman Legionary Cavalry Officer's Iron Prick Spur 1st - 2nd Century A.D From Emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius & Nero to The Era Of Emperors Trajan & Hadrian
In very nicely preserved condition. A good heavy grade quality and rare piece from Imperial Rome.
Imperial cavalry (30 BC – 476 AD)
When the Republic transitioned into the Empire, Augustus made a regular Auxilia corp of non-citizen soldiers. These professional Roman soldiers, like the Legions, were subjects recruited from the non-citizens in provinces controlled by Rome that had strong native cavalry traditions. These men, unlike the Allied Foederetii cavalry, were a regular part of the Roman army and were paid and trained by the Roman State. Arrian describes them as well-equipped and performing well-executed manoeuvres. A typical cavalrymen of the Ala would be paid 20 percent more than a typical citizen legionary.
Roman Auxilia cavalry were usually heavily armoured in mail and armed with a short lance, javelins, the Spatha long sword, and sometimes bows for specialist Horse archer units. These men primarily served as Medium missile cavalry for flanking, scouting, skirmish, and pursuit. As opposed to more modern cavalry units where the horses were kept in stables separate from the riders, Roman cavalry housed the riders and horses in the same barracks.
Although Augustus created regular Auxiliaries, irregular allied forces were still used. For example, Marcus Aurelius recruited Sarmatian allied cavalry to be stationed in Britain. By the 4th century, Romans relied heavily on irregular allies from the migrating Germanic tribes and the Huns.
Augustus, Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), was also known as Octavian, and was the founder of the Roman Empire. He reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult, as well as an era of imperial peace (the Pax Romana or Pax Augusta) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century.
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37, was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Claudius Nero and his wife, Livia Drusilla. In 38 BC, Tiberius's mother divorced his father and married Augustus. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus's two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus's successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat, and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for the empire's northern frontier.
Caligula, Gaius Caesar Augustus Germanicus was Roman emperor from AD 37 until his assassination in AD 41. He was the son of the Roman general Germanicus and Augustus' granddaughter Agrippina the Elder, members of the first ruling family of the Roman Empire. He was born two years before Tiberius was made emperor. Gaius accompanied his father, mother and siblings on campaign in Germania, at little more than four or five years old. He had been named after Gaius Julius Caesar, but his father's soldiers affectionately nicknamed him "Caligula" ('little boot')
Caligula's sister, Agrippina the Younger, wrote an autobiography that included a detailed account of Caligula's reign, but it too is lost. Agrippina was banished by Caligula for her connection to Marcus Lepidus, who conspired against him.170287Caligula also seized the inheritance of Agrippina's son, the future emperor Nero. Gaetulicus flattered Caligula in writings now lost. Suetonius wrote his biography of Caligula 80 years after his assassination, and Cassius Dio over 180 years after; the latter offers a loose chronology. Josephus gives a detailed account of Caligula's assassination and its aftermath, published around 93 AD, but it is thought to draw upon a "richly embroidered and historically imaginative" anonymous biography of Herod Agrippa, presented as a Jewish "national hero".286 Pliny the Elder's Natural History has a few brief references to Caligula, possibly based these on the accounts by his friend Suetonius, or an unnamed, shared source. Of the few surviving sources on Caligula, none paints Caligula in a favourable light. Little has survived on the first two years of his reign, and only limited details on later significant events, such as the annexation of Mauretania, Caligula's military actions in Britannia, and the basis of his feud with the Senate
Claudius, Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italy.
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68.
Nero was born at Antium in AD 37, the son of Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Agrippina the Younger (great-granddaughter of the emperor Augustus). Nero was three when his father died.1 By the time Nero turned eleven,2 his mother married Emperor Claudius, who then adopted Nero as his heir. Upon Claudius' death in AD 54, Nero ascended to the throne with the backing of the Praetorian Guard and the Senate. In the early years of his reign, Nero was advised and guided by his mother Agrippina, his tutor Seneca the Younger, and his praetorian prefect Sextus Afranius Burrus, but sought to rule independently and rid himself of restraining influences. The power struggle between Nero and his mother reached its climax when he orchestrated her murder. Roman sources also implicate Nero in the deaths of both his wife Claudia Octavia – supposedly so he could marry Poppaea Sabina – and his stepbrother Britannicus.
With his death, the Julio-Claudian dynasty ended. Chaos would ensue in the year of the Four Emperors.
4 inches x 3.5 inches, 2 inch long spike . read more
495.00 GBP
Roman-British Cobra Head Brooch, With Amber Glass Eyes. Combined With A Swan's Neck and Head Loop Ist - 2nd Century AD.1900 to 2000 Years Old
Britain was part of the Roman Empire for over three and a half centuries. From the invasion under the emperor Claudius in AD 43 until rule from Rome ended in the early 5th century, the province of Britannia was part of a political union that covered most of Europe.
Roman administration in Britain lasted about 370 years – the same length of time as between now and the end of the English Civil Wars in 1651. It was a complex era of frequent change, which spanned the reigns of more than 80 emperors and saw periods of peace, prosperity and expansion, as well as times of raids, war, fear and recession.
The Romans brought many things to the lands they conquered, including towns, roads, permanent military garrisons and centralised government. In Britain this has left a rich archaeological legacy, from villas and towns to forts and the magnificent Hadrian's Wall.
During Julius Caesar’s military campaigns in Gaul between 58 and 50 BC, he mounted two expeditions to Britain. The first, in 55 BC, was simply an armed reconnaissance, but the second in 54 BC was a serious attack that subdued the major tribes in south-eastern Britain. The Romans didn’t stay, but several tribes may have become friendly ‘client states’, in some respects still independent but also subordinate to Rome.
For almost a century afterwards, tribal rulers in southern Britain maintained diplomatic relations with Rome and traded across the English Channel with its provinces. However, during the first 40 years of the 1st century AD, the Catuvellauni tribe, based to the north and east of London, gradually gained power over neighbouring tribes, the Trinovantes and the Atrebates. This gave them control of territory further south, and also forced the expulsion from Britain in AD 42 of Verica, the pro-Roman king of the Atrebates.
The Catuvellauni’s growing anti-Roman stance coincided with the emperor Claudius’s desperate need to consolidate his fragile hold on power. The usual way for emperors to shore up support was by military victory. So, the invasion of Britain was planned, with the treatment of Verica and the Atrebates as the pretext. Claudius sent an army in AD 43.
How much difference the Roman conquest made to everyday life varied from place to place. In the far West, Wales and most of the North, the army always remained at the forefront of daily life. Soldiers occupied a network of forts, connected by good roads, to police this huge area, in which Roman ways of life had far less impact than in the Midlands, South and East. In those areas, urban civilisation developed. Camulodunum was initially the province’s main town, though Londinium quickly replaced it.
There was never a massive influx of ‘Romans’. The people living in Britannia across the period of Roman rule were mostly the descendants of the pre-Roman tribes, and they lived and worked mainly in the countryside. There was a veneer of Roman officials, while the troops were originally recruited from provinces across the empire.
There would have been a gradual merging of people and culture in and around towns and forts, but in the countryside perhaps less so. The population was probably between 3 and 4 million, of which the Roman army of occupation comprised of up to 50,000 men, almost 2/3rds of the size of the British Army regulars today but 1800 years later. Which currently, strategically, would possibly, be sufficient to defend the Isle of Wight, but not much else.
Picture in the gallery of a Roman silver plaque where the male figure on the right is wearing a similar shaped robe brooch upon his right shoulder. read more
395.00 GBP
A Beautiful and Original Antique Mandingo Chieftain's Slave and Gold Trader Sword With Tattoo'd Leather Scabbard
In superb condition for age, with amazing traditional leather work, wonderfully cared for.
Traditional antique African tribal weaponry are incredibly sought after today, especially as unique pieces of interior decoration to display their beauty and historical appeal
A chieftain's weapon of Mandingo slave and gold traders. The Manding (Mandingo) are West African people. Their traditional sword for the slave traders comprises a sabre like blade, guardless leather grip and scabbard with exquisite leather work.
This example is a long sized example, of a high ranking Mandingo, of very nice quality and finely tattooed. inches long curved blade, leather grip and leather scabbard with leaf shaped widening tip, entirely tooled tattooed and decorated. Of special interest is the finely bound and decorated leather work. These weapons are well known for their leather-work and the tattooing applied to the leather of the scabbards. The iron work skills are typical of the region and period. Many blades are taken from European weapons such as sabres and cutlasses.
While the Baule are a distinct tribal group to the west, it is important to observe that Malinke is a variant term applied to the Mandingo (also Manding, Mandin, Mande).
In general, these remain primarily considered Mandingo weapons, and from regions in Mali. These were of course invariably mounted with European sabre blades. Mandingo Tribe (also known as the Mandinka, Mande, or the Malinke Tribes) were the traders of the African West Coast, trading primarily in gold and slaves from other African tribes.
30 inches long overall in scabbard, blade 23 inches long read more
595.00 GBP
A Truly Exceptional & Rare Original 16th Century Italian Renaissance Sfondagiaco Eared Dagger, Named From The Protruding Twin ‘Ears’ of the Pommel Shaped As Stunning Masked Horned Goats.
An original and rare dagger used by Princes, Dukes and Kings, capable of perforating chainmail and sliding between metal armour plates.
An exceptionally rare and important so called 'Ear Pommel Dagger', from 16th century Venice, Italy. With a traditional form brass hilt, of twin plates double rivetted through the blade tang, finely engraved, with a pair of ear pommels, in the form of two simply stunning full relief masks of horned goats, backed with clam shell decoration. Double edged graduating blade.
What has been described the most valuable dagger in the world was another, most similar 'Ear Form Pommel Dagger', from the same era of the 15th century.
It was from the Nasrid dynasty in Spain and it sold in Sotheby's Auction house nine years ago for an incredible $6 million dollars. However that example was decorated with Islamic decoration in gold. Ear Daggers are considered the most important contribution to the Nasrid panoply of arms and armour. Ear Daggers probably originated from North Africa, although ancient Asiatic versions existed from 1200 bc. They were used in Spain during the 15th and 16th centuries, and also introduced to Italy and Christian Europe in the 15th century. Daggers of this type were once extremely fashionable among great and powerful nobles, princes and kings, and there exists a portrait of the young King Edward VI of England, now in the Royal Collection at Windsor Castle, clutching an Ear Dagger at his waist. Deriving its name from the striking design of the hilt pommel, the Ear Dagger (dague oreilles in French and alla Levantina in Italian) comprises two flattened, embossed or conical discs which resemble ears, issuing from either side of the grip a.
Only a handful of comparable examples of the Nasrid daggers exist, and mainly in museum collections.
Original 15th century ear daggers are only generally to be found in the finest national museums such as the Louvre, the British Royal Collection, the Metropolitan Museum, Fifteenth-century Italy was unlike any other place in Europe. It was divided into independent city-states, each with a different form of government. Florence, where the Italian Renaissance began, was an independent republic. It was also a banking and commercial capital and, after London and Constantinople, the third-largest city in Europe. Wealthy Florentines flaunted their money and power by becoming patrons, or supporters, of artists and intellectuals. In this way, the city became the cultural centre of Europe, and of the Renaissance. Italian Wars, (1494-1559) series of violent wars for control of Italy. Fought largely by France and Spain but involving much of Europe, they resulted in the Spanish Habsburgs dominating Italy and shifted power from Italy to north-western Europe.
The wars began with the invasion of Italy by the French king Charles VIII in 1494. He took Naples, but an alliance between Maximilian I, Spain, and the pope drove him out of Italy. In 1499 Louis XII invaded Italy and took Milan, Genoa, and Naples, but he was driven out of Naples in 1503 by Spain under Ferdinand V. Pope Julius II organized the League of Cambrai (1508) to attack Venice, then organized the Holy League (1511) to drive Louis out of Milan. In 1515 Francis I was victorious at the Battle of Marignano, and in 1516 a peace was concluded by which France held onto Milan and Spain kept Naples. Fighting began in 1521 between Emperor Charles V and Francis I. Francis was captured and forced to sign the Treaty of Madrid (1526), by which he renounced all claims in Italy, but, once freed, he repudiated the treaty and formed a new alliance with Henry VIII of England, Pope Clement VII, Venice, and Florence. Charles sacked Rome in 1527 and forced the pope to come to terms, and Francis gave up all claims to Italy in the Treaty of Cambrai (1529). By the Peace of Cateau-Cambr?sis (1559), the wars finally ended. 16 inches long overall, blade 11 inches. read more
9975.00 GBP
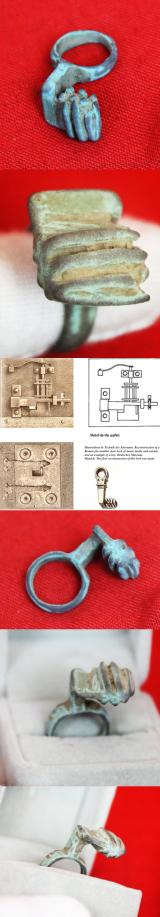
Roman Key Ring, A Bronze Amulet-Ring Key. 1st to 3rd Century A.D.Around 1900 to 1800 Years Old. Worn From The Period of Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius, Lucius Verus, & Commodus
Ancient Roman bronze key ring, an intriguing piece of functional jewellery.
For lack of pockets in their togas, the ancient Romans often wore keys to important boxes, etc on their fingers. The most intriguing items of Roman security hardware seem to be keys and lock bolts. Keys were used mainly for doors, chests, boxes, caskets, cupboards and padlocks. Less often they were used for ceremonial or decorative purposes, such as matron keys, jewelry items and votive offerings.
It is alleged that some ring keys were worn by women as symbols of household authority, as "keeper of the keys". This is probably true, but such are difficult to identify as having served that purpose. The wooden Egyptian pin tumbler locks were over two thousand years old by this time. Roman engineers modernized them and other lock constructions by replacing the wooden parts with corresponding parts made of metal.
The clumsy Egyptian pin tumbler locks were transformed into elegant Roman pin tumbler locks of steel, fitted with an ingenious Roman invention, steel springs. The locks were often tiny masterpieces in terms of both precision and design. All Roman door locks can only be opened from one side. There were illustrations in Le case e monumenti di Pompeii, four volumes by Fausto and Felice Niccolini, printed in Naples in 1854–96. Another author, Albert Neuburger, used the same images in his book on ancient technology, Die Technik des Altertums, printed in Leipzig in 1921. The cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum were buried in ash when the nearby volcano Mount Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD, and were eventually forgotten.
Likely worn over the first knuckle before the second, knuckle position, or around the neck as an amulet
Illustrations in Technik des Altertums. Reconstruction of a Roman pin tumbler door lock of metal, inside and outside, and an example of a key. Deutsches Museum, Munich. The first reconstruction of this lock was made by Louis Jacobi (1836–1910) for the Saalburg Museum north of Frankfurt.
For example; With regards to some expert conservation methods of bronze objects {and some other materials} The dirt from the surface of the object could be removed manually using a scalpel under magnification. Care would be taken not to dislodge the powdery, corroding surface. Where the surface was in particualrly bad condition the dirt will be left in situ and small areas might be locally consolidated using 2.5% HMG Paraloid B72 (methyl ethyl methacrlylate) in 50:50 Acetone (propan-1-one/dimethyl ketone) and Industrial methylated spirits (ethanol,methanol). read more
175.00 GBP
A Superb Crimean War and US Civil War Period Crystal Masonic Gaming Tumbler
A good size crystal gaming tumbler, engraved with numerous Masonic symbols, including the square and compass, with three gaming dice sealed within the glass hollow base.
Circa 1850's.
After 4 years of war, the weary and almost defeated Confederate Army was retreating and leaving the Confederate capital of Richmond to its own fate. As the army retreated, fires broke out in all sections of the city. Hoodlums, deserters, and criminals, with no law and order, began to pillage the city.
Just as the city seemed to be doomed, a Union cavalry unit swung up Franklin Street. The bearded colonel looked warily at the riff raff around him who were about to fire a building which bore a sign "Masonic Hall." Taking command of the moment, he halted his troopers and ordered that an adjutant "have all Masons wheel out of column." Almost half of his force moved out. From this group he ordered a suitable guard to protect the Masonic Temple. The column reformed and resumed its ride. Later General Godfrey Weitzel, a Mason, gave the order, after a request by the Lodge, to continue the guard. The building saved is said to have been the oldest purely Masonic building in America with records dating back to 1787, and the historic building itself was built in 1785 by Richmond Lodge 10. The Grand Lodge assembled here after its formation in Williamsburg until its move in 1869.
In the battle for Galveston, Texas a young Union naval officer who was a Mason was killed on board one of the Union vessels.
An armistice was sought and given for his burial at sea and his father, a Confederate officer, attended the funeral on board.
It was an April morning three days after General Robert E. Lee had surrendered to General U.S. Grant. The Southern troops, led by General John B. Gordon, a Mason, were marching in columns towards the Northern troops who were standing in formation waiting for the Southerners to stack arms and fold their flags. Suddenly a shifting of arms is heard. Gordon looked up with alarm. There was nothing to fear. General Joshua Chamberlain had ordered his troops to assume the position of "honor answering honor." Immediately, the Confederate troops snapped to attention and returned the honor. It was the first act to heal the wounds of a nation that had spent four years and 618,000 lives in civil war. That command of "honor answering honor" was ordered by a Mason.
Major General Joshua Chamberlain was a member of United Lodge 8, Brunswick, Maine. After the war, he became Governor of Maine from 1866-1871 and President of Bowdoin College from 1871-83. read more
295.00 GBP
Most Incredible & Finest Quality King George IIIrd Napoleonic Wars Scottish Presentation Sword, Presented In The Months Following the Battle of Trafalgar The Regiment of Midlothian Infantry, East Midlothian, By the Officer's & Men of The New Battle Co.
This is a magnificent ‘royal grade’ museum piece, a sublime quality presentation sword, made with the finest copper-gilt mounts, silver panels, and a stunning blue and gilt blade with deluxe engraving and etched presentation panel. A sword of the highest rank, commissioned to be hand made by Mr Phillip Rundell & Mr George Bridge, partners of their company of personal goldsmiths to King George IIIrd, and one of the worlds finest makers of objects of magnificence, including the British Crown Jewels, universally recognised as the finest, and most valuable by far, suite of royal regalia in the world.
Formerly in the world famous Smithsonian Collection in Washington, America, sold by them over 25 years ago to raise an urgent need of funds.
In the days it was commissioned it would have been made for the equivalent and likely same cost of the £100 Lloyds Patriotic Fund Presentation Swords, that were presented to the heroes of the Royal Navy, such as that fought at Trafalger etc. Bearing in mind the value of £100 in 1806 was a simply remarkable sum, for example only 6% of the families in Britain had a total income of £100 in an entire year in 1806, an equivalent today of around £80,000.
Presentation inscription motto etched onto the blade reads;
‘Into whose hand
this sword is put,
It’s hop’t will not
fear Buonaparte,
So draw me out
I shine so clear
and if I strike
my foes may fear”
This fabulous sword, was made by Philip Rundell and George Bridge whose company later made The British Imperial State Crown, the most famous and important royal crown of state ever made, and last used by her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II for her coronation in 1953. This wondrous sword was formerly from the Smithsonian Collection in Washington, and is remarkably similar to the most valuable and highest quality presentation British swords of the Napoleonic Wars, the Lloyds Patriotic Fund sabres, that today can fetch up to £220,000, considerably more than they were achieving 40 years ago when we sold a fine £100 pound Lloyds sword, and even 20 years ago when we sold our last Lloyds £100 pound sword. This sword's makers were King George IIIrds personal goldsmiths, and made the Irish Crown Jewels in 1830, and Queen Victoria's Imperial State Crown " expressly made for the solemnity of the Coronation" That was last used by Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth IInd for her coronation. This spectacular sword is inscribed that its bearer should fight Napoleon Bonaparte without fear, but his foes The French will fear its startling brightness and beauty. It has a sharply curved blade, decorated with stands of arms, a crowned GR cypher, the king's Royal arms, a figure of Britannia, and the motto see photo in the gallery and another further Scottish regimental presentation panel on the opposing side of the blade see photo. The dedication reads;
Presented by the New battle company of
The Eastern Regt. of Midlothian Volunteer
Infantry, to David Wight Esq, their Captain
as a Mark of their Regard and Esteem, 1806
It has a superbly detailed classically styled stirrup hilt decorated with acanthus scrolls, oak leaves and acorns, with the langets decorated with stands of arms, it has a copper gilt simulated wire and ribbon bound grip, contained in its ornately mounted silver and copper gilt leather scabbard, each mount finely engraved and decorated with acanthus leaf bouquets and featuring a central oval silver plaque decorated with stands of arms, the upper mount with maker's panel. This amazing sword was formerly in the collection of the Smithsonian in Washington, USA, bequeathed to them by a famed American collector of Napoleonic arms, which they sold for the benefit of the Smithsonian's funds over 25 years ago. Blade 75 cm approx. Maker marked by Philip Rundell and George Bridge of London. The firm was appointed as one of the goldsmiths and jewellers to the king in 1797 and Principal Royal Goldsmiths & Jewellers in 1804, and the firm held the Royal Warrant until 1843. They served four monarchs: George III, George IV, William IV and Victoria. After the Congress of Vienna (1814–1815), the firm prepared 22 snuff-boxes to a value of 1000 guineas each to be given as diplomatic gifts.
In 1830–1831, the firm created the Irish Crown Jewels from 394 precious stones taken from the English Crown Jewels of Queen Charlotte and the Order of the Bath star of her husband George III, and Queen Victoria's Imperial State Crown for her coronation. Despite the incredible success of the Battle of Trafalgar, and the routing of Napoleon’s French and Spanish fleet by Admiral Nelson, concern was still great amongst the people of Britain, in fact it was never greater, of the fear that Bonaparte would continue his efforts to confound and attempt to conquer Britain and its empire, and thus to create his own empire controlling all of Europe And Russia. Rundells quality of workmanship was so fine and renowned throughout the world that there are over 100 items by Rundells in the Royal collection alone.
This wonderful sword was obviously worn with pride by its recipient officer, thus the blade shows commensurate signs of light surface wear as to be expected.
We can, if required, commission a contemporary, bespoke glazed & framed display cabinet made by our local specialist artisan. Perfectly suitable for table or wall mounting. With several options of wood framing types, such as gilt, black or silver, also with coloured velvet backing options, and a suitably engraved brass plaque if required.
The scabbard has a blank silver panel on the inner throat mount that could have been presentation engraved but hasn't been read more
36950.00 GBP
A Wonderful, Original, German 'Zweihander' Great Sword, 16th Century. Probably The Most Impressive And Largest Sword Ever Used in Historic Warfare. Following the Form of Sword Made Famous By The Scots in The Time Of Sir William Wallace
This Spectacular Original Great Sword, just a half inch under six feet long, is a simply stunning original antique artefact of history, that is also a remarkable 'statement' piece. It is taller than the average man, and worthy of a primary display position in any noteworthy location, wether albeit in a castle, an armoury, museum or a private home, this piece displays its dramatic form with grandeur and nobility alongside great beauty.
We consider ourselves very lucky indeed if we are able to acquire such a fabulous type of sword available on the collectors market today
Around 500 years old, this ‘Great Sword’ is a later example of their earliest most famous appearance in the great wars in Scotland against the English, during the reign of Edward Ist, the principle of the original design and use of the ‘Great Sword’ remained the same for around 300 years.
Effectively it is the weapon of the so called ‘berserker’ warrior, who was skilled at running full pelt at the enemy positions, with the spinning great sword rotating above his head, terrifyingly clearing a way through defensive pikemen and the such, in order for the offensive charge of his fellow infantry and cavalry warriors behind him to breakthrough the defensive enemies ranks.
This is a most incredible and stunningly beautiful example of its type, with a long early straight double-edged blade, tapering to a sharp point and formed with a pair of near full length fullers on each face, struck with a brass inlaid running wolf mark on one face (with small hairlines and overall a natural russetted surface) rectangular ricasso with engraved border, struck with a series of armourers' marks on each side including a Pi and cross and orb, and crowned head with running wolf in gold. The armourer’s mark representing the blade work of Johannes Wundes, and all of these armourers marks are indicative of his fine work. The sword is fitted with a later crescentic defensive hooked, iron cross-guard, comprising pair of drooping quillons with tightly scrolling terminals each with an additional lug front and back, formed en suite. An inner and outer ring-guard each filled with a fleur-de-lys, fluted globular pommel, decorated throughout with scrolls, and designed for the Landsknecht Mercenary Foot Knights, for use as a hugely effective, offensive sword, and, as we previously described, swung around the head in a fast rotational movement [in essence, just like a helicopter blade] to create a twelve foot circle of terror and destruction.
An experienced Landsknecht warrior could be designated a Doppelsoldner, an armoured foot soldier who served as the backbone for the armed formation in battle (and was paid double for it) and also, in addition to being armed with the pike, as more recent recruits, they could also be alternatively employed wielding a 6-to-8-foot-long (1.8 to 2.4 m) halberd or partisan, or, more famously, a Zweihander (literally: "Two-hander") such as this sword, a two-handed sword as long as 180 cm (6 ft). These great war swords could be swung in a great circular arc [somewhat akin to a helicopter motion] and thus, incredibly effectively, used to knock the forward pointed long pikes, held by enemy pikemen, aside, that were wielded by a phalanx of pikemen, thus creating disorder among the tightly-arranged enemy pikemen in order to break through their lines.
However, another primary use of the two-handed sword, would be to serve as the 'guard' for the standard bearer, for it is a weapon that allows for a few to oppose many.
The Swiss adversaries to the Landsknechts had specifically attempted to prohibit the use of these swords during the late 15th century, as they deemed them unsuitable for the constricted manner of pike warfare.
The handle grip, is now in appearance, showing just the narrow all steel blade tang, but, would originally been leather bound, over partial wood, and leathered right down to the cutting edge of the blade. The original leather and wooden grip would never survive intact for 500 years, being organic it has little ability to last for so many centuries.
52 1/8 in blade, 71.5 inches long overall read more
9500.00 GBP
Superb Napoleonic Wars, British Officer's Sabre With Captured French 'Trophy' Mamluk Consular Guard Officer's Damascus Blade, With An Ancient Egyptian Serpent Goddess Hilt. For an Officer Who Served in The Nile Campaign
New photographs added to include the identical Damascus blade, bearing a Mamluk officer's portrait bust within its design, of the Philippe Missilier Collection exceptionally rare sword of an officer of the Mamluk Imperial {formerly Consular} Guard, Ist Empire, {see photo 9 in the gallery}
Gilt bronze entwined twin serpent zoomorphic hilt, influenced by the Egyptian Goddess Wadget, chisselled in great detail and of very fine quality. Talisman symbolic, Napoleonic Damascus blade, of an officer of the elite Napoleonic Mamluke Guard Circa 1800. There is another blade known, an identical example, on another sword from an officer of the French Napoleonic Mamluke Guard, formerly in the Philippe Missillier collection, that appears in Aries seminal work on French Napoleonic swords, and Michel Pétard's work of similar renown, with all the same iconography within the design, and, also upon a damascus blade {see photo 9 in the gallery}.
This sword is extraordinarily rare, as the officer corps of Napoleon's Mamluk Consular Guard would likely number less 15. For example in 1802 there were just 13 officers recorded who would have carried this sword, and how many survive to today, may possibly be less than two or three.
Certainly a war trophy blade and scabbard used by a British officer that served at the Battle of the Nile, thus, it also has Nile Club connections. There are numerous examples of snakes depicted in zoomorphic hilted Napoleonic swords, such as the Lloyds Patriotic Fund swords, but usually combined with other beasts, such as lions, tigers or hounds, but to have two opposing entwined serpents is very rare indeed. Without a doubt this hilt design was inspired by Wadjet, the ancient Egyptian serpent goddess, in order to reflect the direct connection to a Battle of the Nile British officer veteran.
Snake sculpture - the Staff of Aesculapius, the Staff of Mercury, and the Embodiment of Wisdom Snakes are fairly frequent in Georgian sculpture, and of course from other periods. In art generally in fact from medieval times onwards, the snake is also associated with wisdom, and in this capacity is often found with statues of Prudence. The way this sword is constructed shows it is a trophy blade, of a Mamluk officer, thus captured in combat by the British, and then re-mounted. The Mamluk officer’s sword, was etched with talismanic symbols of a crescent moon, sun, a Mamluks turbaned officers portrait bust head, and a stand of arms, upon fine Damascus pattern steel.
In fact the whole sword may indeed now be described as iconically talismanic. The blade is in superb condition, with its original steel combat scabbard, also in excellent condition, and the English zoomorphic hilt is, furthermore, excellent too .
Egyptian gods and goddesses, much famed in ancient Egypt, become hugely popular throughout Western artistic culture in the early 19th century.
Europe became beguiled by ancient Egyptian art and architecture in all its forms, and furniture designers and sculptors particularly, eagerly created the ‘Egyptian style’ in the Regency period England, and the Consular and Directoire period in France.
The Nile Club" (often referred to historically as the Egyptian Club) was an exclusive group of senior British officers who fought under the command of Rear-Admiral Sir Horatio Nelson at the decisive Battle of the Nile on August 1–3, 1798.
Key details regarding this group and its connection to the Napoleonic Wars include:
Following their massive victory at Aboukir Bay, which stranded Napoleon in Egypt, the captains of Nelson’s fleet formed this most exclusive club to celebrate and commemorate the action.
The club included the captains of the ships present at the battle, such as Captains Sir F. Berry (Vanguard), T. Trowbridge (Culloden), R.W. Miller (Theseus), and A.J Ball (Alexander).
The "Nile" Dirks/Swords: Members were entitled to wear a special sword or dirk featuring a zoomorphic Nile Crocodile on the hilt to signify their participation. Marines and Army may have had the associated Egyptian zoomorphic snake god hilt, or, another option, the zoomorphic camel head hilted sabre. We had a zoomorphic Nile Club camel head hilted officer’s sword a few years ago that we sold to an esteemed American dealer.
These weapons are now considered very rare historical artifacts.
Connection to Trafalgar: Many of the officers in the Nile Club continued to serve under Nelson and were likely present at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, where they would have worn their Nile-associated swords with pride.
The Mamluks service in the Napoleonic Wars;
At the Battle of Austerlitz, the Mamluks were in the reserve, under Rapp, with the rest of the Imperial Guard cavalry, when the Russian cavalry charged onto the Pratzen Heights and dispersed two French regiments of the Vandamme division. After an unsuccessful counterattack by two squadrons of mounted chasseurs supported by three squadrons of mounted grenadiers, Napoleon ordered Rapp to charge at the head of the last two squadrons of chasseurs and the Mamelukes in order to restore the situation. The Mamelukes threw themselves into the mêlée, but the impact of their charge was mitigated by the mass of men and horses. Lieutenant Renno rushed at a Russian square and opened a breach, which was quickly exploited by the Mamelukes, who broke through the formation and took 120 prisoners. Encouraged by this success, Rapp's cavalrymen seized a battery before contributing to the rout of the Russian Imperial Guard cavalry. Following this victorious engagement, two Mamelukes each came to throw an enemy standard at Napoleon's feet. The company's losses amounted to one dead and five wounded.
In 1808, Napoleon ordered Marshal Murat to enter Spain and occupy Madrid. The Mamluks took part in this expedition. Staunchly Catholic, the Spanish people remembered the period of Muslim rule in the Iberian Peninsula by the Moors, and was offended by the presence of the Mamluks who entered the capital on 24 March 1808. The abdication of King Charles IV and then of his son Ferdinand in favour of Joseph Bonaparte, the Emperor's brother, exacerbated tensions between the Spanish and the French.
In April, the company of Mamluks numbered 86 men. Seeking to expand this force, chef d'escadron Daumesnil, commanding the detachment of chasseurs of the Guard in Spain, asked permission to enlist foreigners, former Mamelukes but also Greeks or Spaniards, which Napoleon refused: "I created this corps to reward those men who served me in Egypt, and not to make a collection of adventurers." On 2 May, the people of Madrid revolted and attacked isolated soldiers. Murat then ordered the cavalry to enter the city to suppress the riot. The mounted chasseurs of the Guard led by Daumesnil advanced first, followed by the Mamelukes and the rest of the Guard cavalry. Passing through Alcalá Street, where they had rocks thrown at them, the French cavalrymen reached the Puerta del Sol where many Spaniards had gathered.
The Mamluks arrival marked the beginning of merciless fighting. The Madrid rebels assaulted the horsemen with knives, jumped onto their mounts behind them and tried to dismount them. For their part, the Mamluks responded with scimitar strikes and skillfully cut off heads, a hundred "in an instant" according to Marbot. In the mêlée, Lieutenant Chahin saved chef d'escadron Daumesnil, who had fallen to the ground after having his horse killed from under him, before being struck in turn; the residents of a house on San Geronimo Street were also massacred by the Mamluks in retaliation for the killing of two of their comrades. At the end of the fighting, the company had its five officers injured as well as three horsemen killed or mortally wounded, losses that Ronald Pawly considered as "relatively limited" compared to the painter Goya's depictions. Edward Ryan instead mentions only two killed.
See picture 8 in the gallery to see Admiral Nelson with his Nile Club zoomorphic hilted sword
Overall in superb condition, Small scabbard throat mount lacking to the scabbard. Overall 39 inches long, blade 32 inches read more
5950.00 GBP
Incredibly Rare To Survive, 2000 Year Old Historic Museum Pieces. Original, Republic & Imperial Roman Military, Legionary's or Centurion's Lorica Squamatae Mail Armour 1st Century
These are small integral pieces of original Roman combat armour, that once discovered have to be recognised for their rarity by such as an archaeologist or ancient Roman military historian or they would never be saved for history, and very likely discarded. Which would be one of the primary reasons that they are so very rare, that, and also because they are thin small plates that have to be originally lost in the correct organic surroundings within which to survive the past two millennia relatively intact.
These small but incredibly rare pieces could look amazing sympathetically bespoke framed.
A super, small collection of original, historical, Imperial Roman, Viking and Crusader's artefacts has just been acquired by us and will be added over the next week or so. Only the third such group of original Roman armour we have seen in 15 years.
A small section panel of an incredibly rare, original Roman military armour mail shirt, around 2000 years old, small pieces but exceptionally historically significant. They would look amazing if nicely framed. Used by both regular Roman Legionaries and high ranking Centurions, Lorica squamata was a scale armour, looking like the skin of a fish. Items such as this were oft acquired in the 18th century by British noblemen touring Northern France and Italy on their Grand Tour. Originally placed on display in the family 'cabinet of curiosities', within his country house upon his return home. A popular pastime in the 18th and 19th century, comprised of English ladies and gentlemen traveling for many months, or even years, througout classical Europe, acquiring antiquities and antiques for their private collections.
A shirt of scale armour would be put on with side or rear lacing and reach to the mid-thigh. The lorica squamatae is a type of scale armour used by the ancient Roman military during the Roman Republic and at later periods. It was made from small metal scales sewn to a fabric backing.
It is typically seen on depictions of standard bearers, musicians, centurions, cavalry troops, and auxiliary infantry, as well as regular legionaries. The somewhat historically inaccurate Roman victory triumph depicting Trajan's victory over the Dacians, the Tropaeum Traiani, shows the majority of legionaries wearing loricae squamatae. A shirt of scale armour was shaped in the same way as a mail lorica hamata, mid-thigh length with the shoulder doublings or cape.
The individual scales (squamae) were either iron or bronze, or alternating metals on the same shirt. They could be tinned as well, one surviving fragment showing bronze scales that were alternately tinned and plain. The metal was generally not very thick, 0.50 mm to 0.80 mm (.020" to .032") perhaps being a common range. Since the scales overlapped in every direction, however, the multiple layers gave good protection. The size ranged from as small as 6.3 mm wide by 9.5 mm tall (1/4" ? 3/8") up to about 5 cm wide by 8 cm tall (2" ? 3"), with the most common sizes being roughly 1.3 cm by 2.5 cm (1/2" ? 1"). Many have rounded bottoms, while others are pointed or have flat bottoms with the corners clipped off at an angle. The scales could be flat, or slightly domed, or have a raised midrib or edge. All the scales in a shirt would generally be of the same size; however, scales from different shirts may vary significantly.
The scales were wired or laced together in horizontal rows that were then laced or sewn to the backing. Therefore, each scale had from four to 12 holes: two or more at each side for wiring to the next in the row, one or two at the top for fastening to the backing, and sometimes one or two at the bottom to secure the scales to the backing or to each other.
There was also a rare type where the backing was a mail lorica hamata, effectively giving two layers of defence, but at the cost of greater weight and expense.
It is possible that the shirt could be opened either at the back or down one side so that it was easier to put on, the opening being closed by ties. Much has been written about scale armour's supposed vulnerability to an upward thrust, but this may be exaggerated.
No examples of an entire lorica squamata have ever been found, but there have been several archaeological finds of very small fragments of such shirts, and individual scales.
The type of armour in which the scales are laced to each other and need no backing at all is known as lamellar armour, while to confuse the matter there is also locking scale in which the scales are wired together without a backing. It can be difficult to tell which type of armour a single scale might have come from, as the Romans did not necessarily have different terms for each type. The typical scale had a vertical pair of holes at each side near the top, plus one or two holes at the top. These armour scales would look superb put together and framed in a display. They are individualy quite small and partially fragmented but easily dwarfed by their historical interest, rarity and significance. Their size and unusual appearance explains much why they are so rarely found, as they are easily corrupted by the centuries once buried, and only identifiable by those that know exactly what they are, thus easily discarded if discovered by the uninformed. As with all our items it comes complete with our certificate of authenticity. read more
645.00 GBP